Software
Pyranges
|
Pyranges is a python library for manipulation of genomic intervals, such as gene annotations, genomic features, and NGS-derived data. Pyranges allows to load and process all genomic intervals as tables (analogous to pandas dataframes), offering highly efficient methods for input/output, calculation of overlaps, subregion retrieval, and much more. Pyranges is co-developed by Endre Bakken Stovner (Norwegian University of Science and Technology) and the Mariotti lab.
Documentation and installation: pyranges.readthedocs.io Source code: github.com/pyranges/pyranges |
Selenoprofiles
|
Selenoprofiles is a pipeline for homology-based identification of selenoproteins in nucleotide databases.
The program accepts input alignments of protein sequences (profiles) and combines blast, exonerate and genewise to identify homologous genes. Selenoprofiles uses a modified scoring scheme to align selenocysteine residues. It also comes with built-in profiles for known selenoprotein families, so that it can predict the set of selenoproteins encoded in a target genome out-of-the-box. Selenoprofiles is available for installation in linux based systems. Documentation and installation: https://selenoprofiles4.readthedocs.io/ Source code page: https://github.com/marco-mariotti/selenoprofiles4/ Citation: Mariotti M, Guigó R (2010) Selenoprofiles: profile-based scanning of eukaryotic genome sequences for selenoprotein genes. Bioinformatics. 26(21):2656-63. Santesmasses D, Mariotti M, Guigó R (2018) Selenoprofiles: A Computational Pipeline for Annotation of Selenoproteins. Methods Mol Biol. 1661:17-28. |
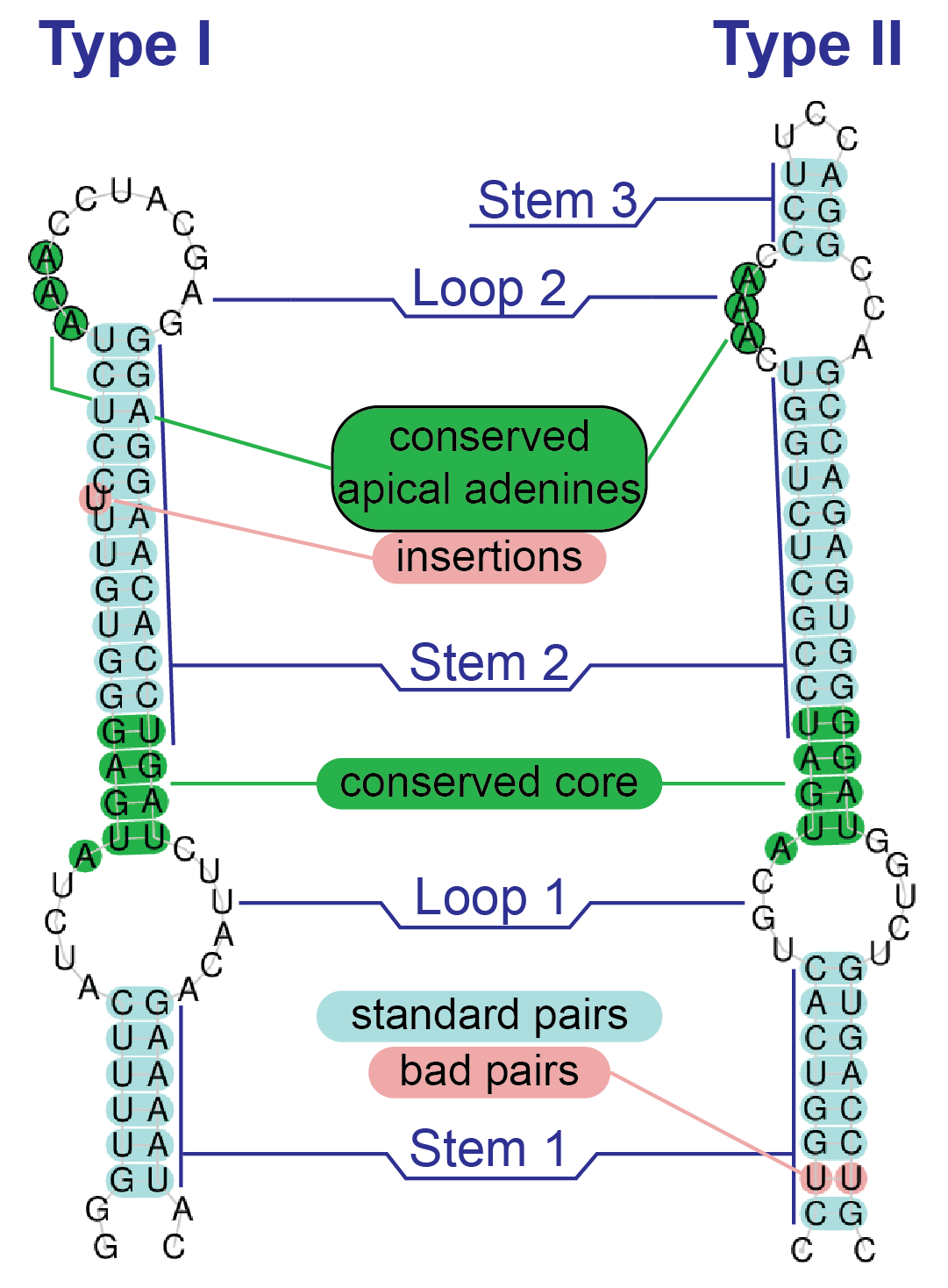
SECISEARCH3 AND SEBLASTIAN
|
SECISearch3 is a pipeline to predict eukaryotic SECIS elements, the essential selenocysteine recoding signal present in the 3'UTR of selenoprotein transcripts.
The program uses a manually curated model consisting of hundreds of SECIS elements, which are searched through Infernal, a method for identification of RNA structural motifs based on homology. SECISearch3 can also use a de novo pattern-based identification method (aka SECISearch1) and a second homology-based method (aka SECISearch2, based on the cove software). The pipeline includes a custom SECIS filter, and also produces images of the predicted SECIS structure highlighting its most important elements. Seblastian is a pipeline to identify eukaryotic selenoprotein genes in nucleotide sequences. It employs SECIS prediction as its first step, then it looks upstream to identify their selenoprotein coding sequence. Seblastian relies on SECISearch3 for the prediction of SECIS elements. Then, blastx is run on the sequence upstream of each potential SECIS, looking for alignments of candidate Sec-encoding UGA codons with annotated proteins. Seblastian can be configured to search for known selenoprotein families, in which case UGA-to-Sec alignments are sought, or it can search for novel selenoprotein families, in which case UGA-to-Cys alignments are analyzed. Understandably, the second use is much less specific and requires validation. Both SECISearch3 and Seblastian are provided freely in a webserver mirrored in two locations. Webserver #1: https://seblastian.crg.es/ Webserver #2: http://gladyshevlab.org/SelenoproteinPredictionServer/ Citation: Mariotti M, Lobanov A V, Guigo R, Gladyshev VN (2013). SECISearch3 and Seblastian: new tools for prediction of SECIS elements and selenoproteins. Nucleic Acids Res 2013;41:e149. Mariotti M (2018). SECISearch3 and Seblastian: In-Silico Tools to Predict SECIS Elements and Selenoproteins. In: Chavatte L, editor. Selenoproteins. Methods Mol. Biol., vol. 1661, Humana Press, New York, NY; 2018, p. 3–16. |
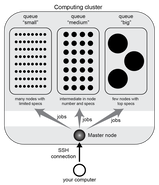
Qjob
|
Qjob is a command line utility for all users of a computing cluster, whether it is for bioinformatics or any other computational task.
The aim of qjob is to simplify the everyday tasks of preparing commands for their execution on a computing cluster. This includes splitting commands into jobs, define job specifications, and submit them for computation. For more information and for installation instructions, visit https://qjob.readthedocs.io/en/latest/ |
Pyaln